Received: February 2019
DOI 10.17677/fn20714807.2019.02.03
Fluorine Notes, 2019, 123, 5-6
Quantum-Chemical Calculation of Some Molecules of Triftoromethylstyroles by the DFT Method
V.A. Babkin1, A.V. Kozhukhova1, D.S. Andreev1, A.V. Ignatov1, A.I. Rakhimov2, N.A. Rakhimova2, V.S. Belousova3, E.S. Titova2,4, A.R. Denisyuk5, K.Yu. Prochukhan6
1Sebryakovsky branch of the Volgograd State Technical University, 403343 Volgograd Region,
Mikhaylovka, Michurin Street, 21
e-mail: babkin_v.a@mail.ru
2Volgograd State Technical University, 400005 Volgograd, Lenin Avenue, 28
e-mail: organic@vstu.ru
3 I.M. Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University (Sechenov University), 119991, Moscow, Trubeckaya Street, 8, building 2
4Volgograd State Medical University, 400131 Volgograd, Pavshich bortcov Square, 1
5Medical College of Volgograd State Medical University, 400001 Volgograd, Kim Street, 18
6Bashkir State University, 450076, Republic of Bashkortostan, Ufa, Zaki Validi Street, 32
Abstracts: A Quantum-chemical calculation of some trifluoromethylstyrene molecules: 2-(trifluoromethyl)styrene, 3-(trifluoromethyl)styrene, 4-(trifluoromethyl)styrene was first performed by the DFT PBE0 method in the 6-311G ** basis. Geometry optimization was performed for all parameters by the standard gradient method. The optimized geometrical and electronic structure of these compounds was obtained. Their acidic force (pKa = 30-32). theoretically estimated. It is established that the molecules belong to the class of very weak H-acids (pKa> 14).
Keywords: quantum-chemical calculation, 2-(trifluoromethyl)styrene, 3-(trifluoromethyl)styrene, 4-(trifluoromethyl)styrene, quantum chemical method DFT:PBE0/6-311G**, acidic force.
Introduction
Fluorine-containing styrenes, as monomers of cationic polymerization for the preparation of polymer products, have not been studied to date. The copolymerization of n-fluorostyrene with isobutylene has been studied experimentally in order to obtain lubricating oils or thickeners for them [1]. The copolymerization was carried out in methylene chloride in the presence of aluminum chloride under various conditions. The product of the greatest molecular weight of 21000 was obtained at –100 C°. Other information on the polymerization of fluorine-containing styrenes, the polymer products of which can be used in medicine and in other fields of science and technology, is practically absent. However, it is necessary to know the conditions for the polymerization of fluorinated styrenes, the catalysts and promoters used, the influence of the nature of the solvent on the mechanisms of elementary acts of polymerization, the geometric and electronic structure of the used fluorine-containing styrenes and active centers.
Methodical Part
The aim of this work is a quantum chemical calculation of some molecules of trifluoromethylstyrene: 2-(trifluoromethyl)styrene (I), 3-(trifluoromethyl)styrene (II), 4-(trifluoromethyl)styrene (III) [2] by method DFTP BE0 in the basis of 6-311G** with optimization of geometry in all parameters by the classical gradient method built into the program Firefly [3], theoretical assessment of their acidic force, elucidation effects on the acidic force of the location of trifluoromethyl in the benzene ring of styrene. The method is partially based on the source code of GAMESS (US) [4]. The calculations were carried out at the approximation of an isolated molecule in the gas phase. The well-known MacMolPlt program was used for visual representation of the molecule model [5].
Results and Discussion
The optimized geometrical and electronic structure, the total energy and the electron energy of the molecules: (I), (II), (III) are obtained by the DFT-PBE0 method in the 6-311G ** basis and are shown in fig. 1-3 and in table 1-4. The acid force value of these molecules was determined by the formula for DFT: PBE0 / 6-311G ** — рКа=51.048-150.078qmaxH+ (qmaxH+= +0,138),
where qmaxH+ — the maximum charge on a hydrogen atom,
рКа —a universal indicator of acidity.
(I): qmaxH+= +0,138, рКа=30; (table 1)
(II): qmaxH+= +0,129, рКа=32; (table 2)
(III): qmaxH+= +0,130, рКа=32; (table 3)
Quantum-chemical calculation of molecules of some trifluoromethyl-containing styrenes: (I), (II), (III) was first performed by the DFT PBE0 method in the 6-311G ** basis with optimization of geometry for all parameters by the standard gradient method. The optimized geometrical and electronic structure of these compounds was obtained. The acid force of the studied styrenes is in the range pKa = 30–32. These molecules belong to the class of very weak H-acids (pKa> 14). Acidic force does not depend on the location of trifluoromethyl in the styrene benzene ring.
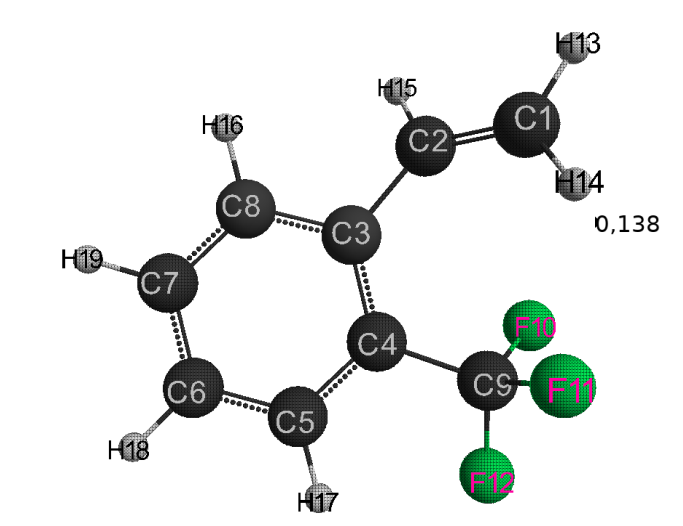
Fig. 1. Geometric and electronic structure of the molecule (I)
(Е0= −1696176 kJ/mol)
Table 1. Optimized bond lengths, valence angles and charges on the atoms of the molecule (I) obtained by the DFT method: PBE0 / 6-311G **.
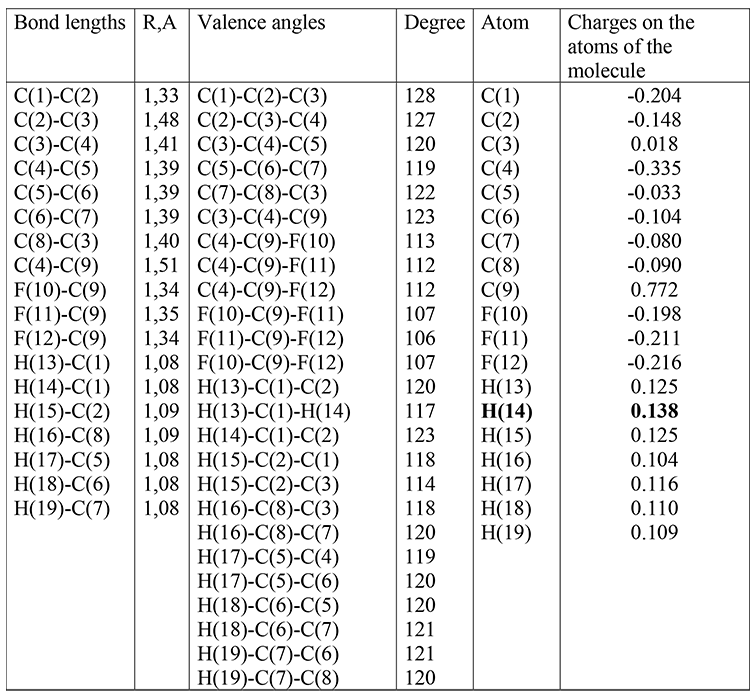
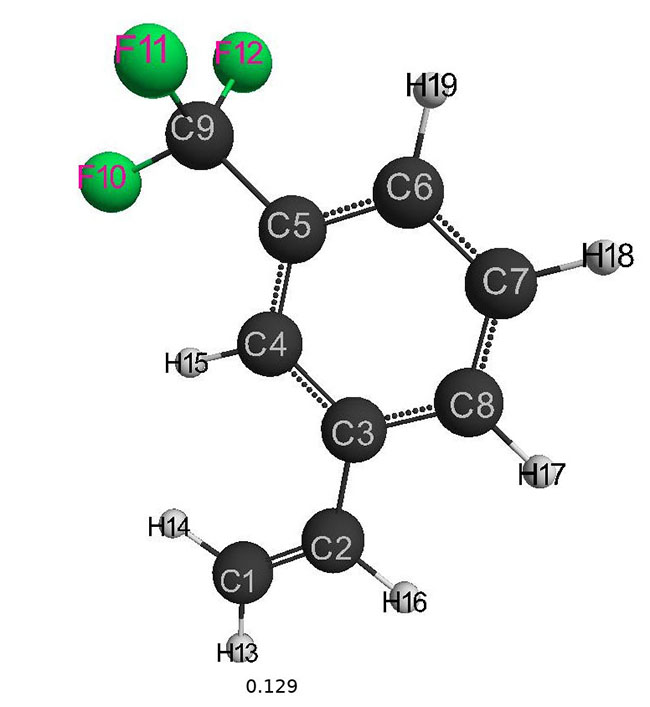
Fig. 2. Geometric and electronic structure of the molecule (II)
(Е0= −1696196 kJ/mol)
Table 2. Optimized bond lengths, valence angles and charges on the atoms of the molecule (II) obtained by the DFT method: PBE0 / 6-311G **.
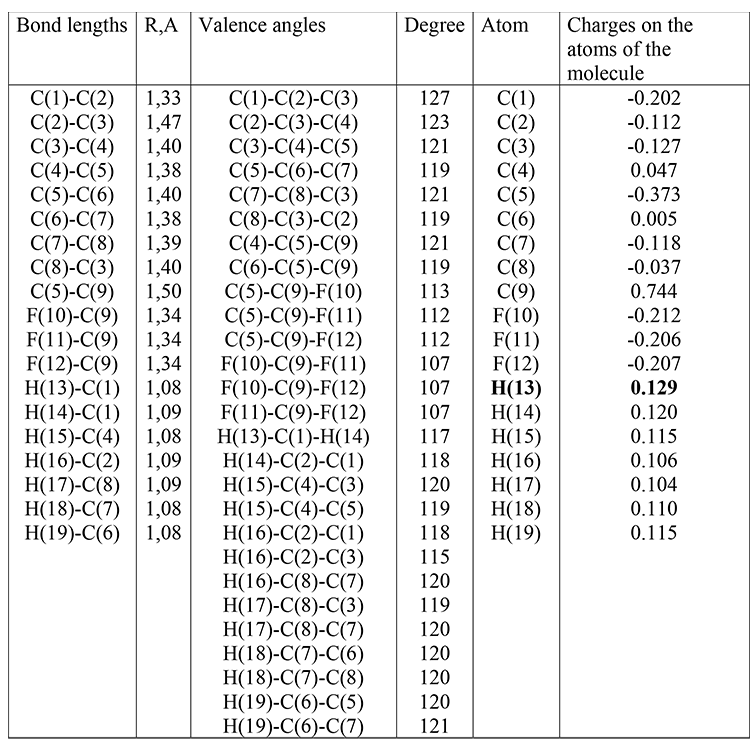
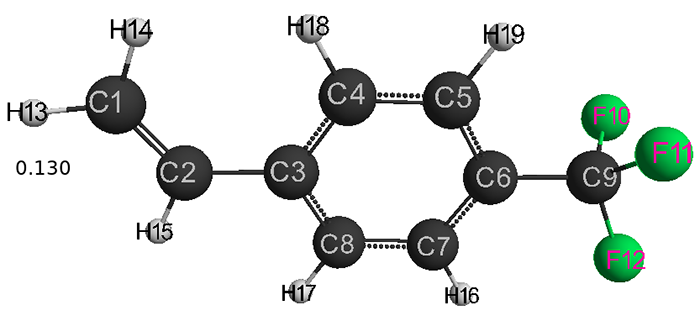
Fig. 3. Geometric and electronic structure of the molecule (III)
(Е0= −1696197 kJ/mol)
Table 3. Optimized bond lengths, valence angles and charges on the atoms of the molecule (III) obtained by the DFT method: PBE0 / 6-311G **.
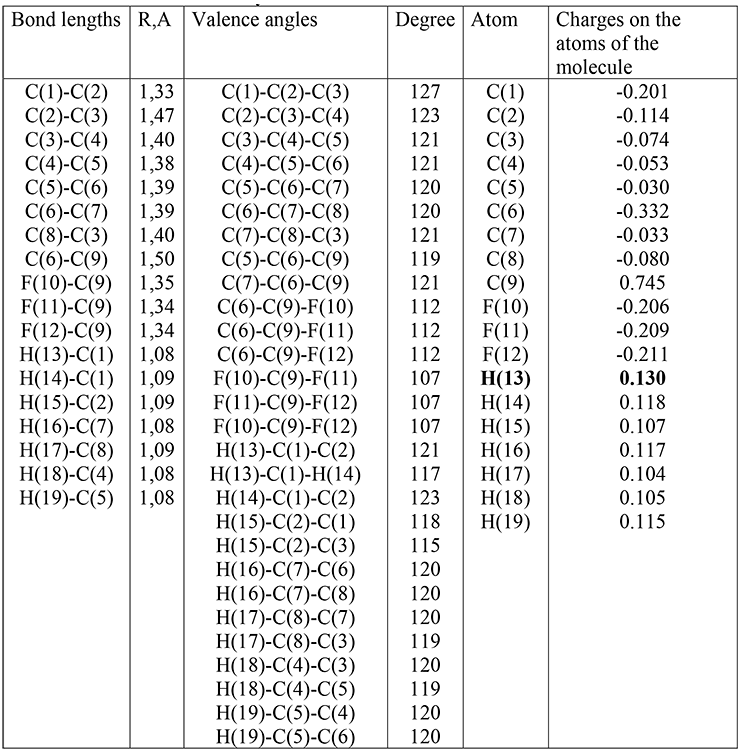
Table 4.The total energy (E0), the maximum charge on a hydrogen atom (qmaxH+), acid force (pKa)
| No |
Fluorine-containing styrenes |
Е0 kJ/mol |
qmaxH+ |
pKa |
|
1 |
(I) |
−1696176 |
0.138 |
30 |
|
2 |
(II) |
−1696196 |
0.129 |
32 |
|
3 |
(III) |
−1696197 |
0.130 |
32 |
References
- F.M. Aliev. The copolymerization of p-fluorostyrene and isobutylene // Azerbaijan Chemical Journal, 1971, p.109.
- J. Kennedy. Cationic polymerization of olefins. / – Moscow, 1978. – 431 P.
- Alex A. Granovsky, Firefly version 8, http://classic.chem.msu.su/gran/firefly/index.html
- M.W. Schmidt, K.K. Baldridge, J.A. Boatz, S.T. Elbert, M.S. Gordon, J.H. Jensen, S. Koseki, N. Matsunaga, K.A. Nguyen, S.J. Su, T.L. Windus, M. Dupuis, J.A. Montgomery. "General Atomic and Molecular Electronic Structure System". Journal of Computational Chemistry, Vol. 14, 1347-1363(1993). doi:10.1002/jcc.540141112
- B. M. Bode, M. S. Gordon. "MacMolPlt: A graphical user interface for GAMESS". Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling, Vol. 16, No. 3, 1998, p. 133-138.
Recommended for publication by Prof. S. M. Igoumnov
Fluorine Notes, 2019, 123, 5-6
